
A research group headed by Profs. GAO Xiaoming and LIU Kun from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a concentration-independent pressure sensing method based on two-color laser absorption spectroscopy for high-temperature combustion diagnostics.
The results were published in Optics Letters.
Aero-engines are moving toward high-temperature, high-pressure combustion to improve thermodynamic efficiency. Pressure is an important parameter to monitor engine performance and diagnose engine failures. However, conventional contact pressure sensors not only disrupt combustion flows, but also suffer from the temperature tolerance limit of sensor materials.
In view of this, the researchers developed the non-contact pressure sensing method for high-temperature environments and demonstrated it at temperatures up to 1,300 K.
They focused on how to address the effect of molecular concentration on gas pressure measurements in high-temperature environments and found that the concentration variable could be eliminated by coupling the collisionally broadened linewidths of two absorption lines.
With this finding, the researchers could realize concentration-independent pressure measurement. Considering that the main product of a hydrocarbon-fueled combustion system is H2O, they validated this finding with two absorption lines of H2O near 1,343 nm and 1,392 nm on a carefully designed heated absorption cell.
"Our results provide a valuable tool for pressure sensing in high-temperature environments and can promote the development of laser-based multi-parameter diagnostics for combustion science," said Prof. LIU Kun.
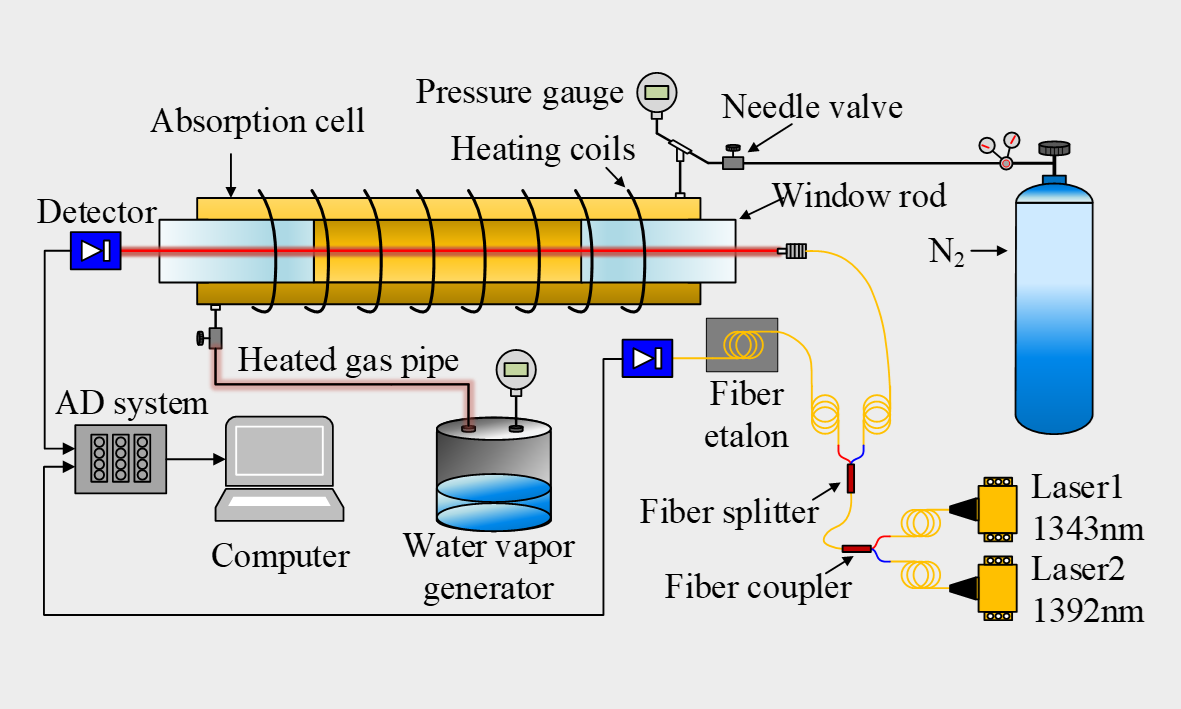
Schematic of pressure measurement using two-color laser absorption spectroscopy in heated absorption cell. (Image by WANG Ruifeng)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

